Fast and Slow Pointers
This technique uses two pointers that traverse the input data at different speeds.
How to Identify
- Data Structure Involves: Array, String, Linked List
- Question Type: When the problem involves something related to cyclic data structures.
Example
Linked List Cycle
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
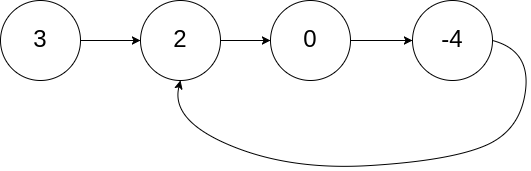
Example
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
Typescript
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
if(!head) return false
let slow = head, fast = head
while(fast.next && fast.next.next){
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if(slow === fast) return true
}
return false
}
Middle of the Linked List
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.

Example
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.
Typescript
function middleNode(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let slow = head, fast = head
while(fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return slow
}
Related Problems
| Problems | Difficulty | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linked List Cycle | Easy |
| 2 | Middle of the Linked List | Easy |
| 3 | Reorder List | Medium |
| 4 | Remove Nth Node From End of List | Medium |